Six Sigma is a game-changing methodology in the modern world of business, where efficiency and quality are paramount. It helps organizations achieve excellence, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction through data-driven decision-making and process improvement.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a disciplined, systematic approach to vary and reduce process variation while eliminating defects. Its origins date back to the 1980s at Motorola and was later popularized in the 1990s by General Electric as the epitome of quality improvement and operational excellence.
The term “Six Sigma” describes a statistical measure: getting to near-perfection with 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO).
Fundamental Concepts of Six Sigma
- Customer Focus: Every Six Sigma project is initiated by grasping customer requirements and ensuring the processes are aimed at meeting customer needs.
- Statistical Decision-Making: It depends heavily on statistical data in finding root causes and validating improvement efforts.
- Process Orientation: Six Sigma focuses more on improving end-to-end processes rather than looking at isolated issues.
- Proactive Management: It encourages the anticipation of problems and the implementation of preventive measures.
- Collaboration and Engagement: Cross-functional teams must participate in successful Six Sigma projects.
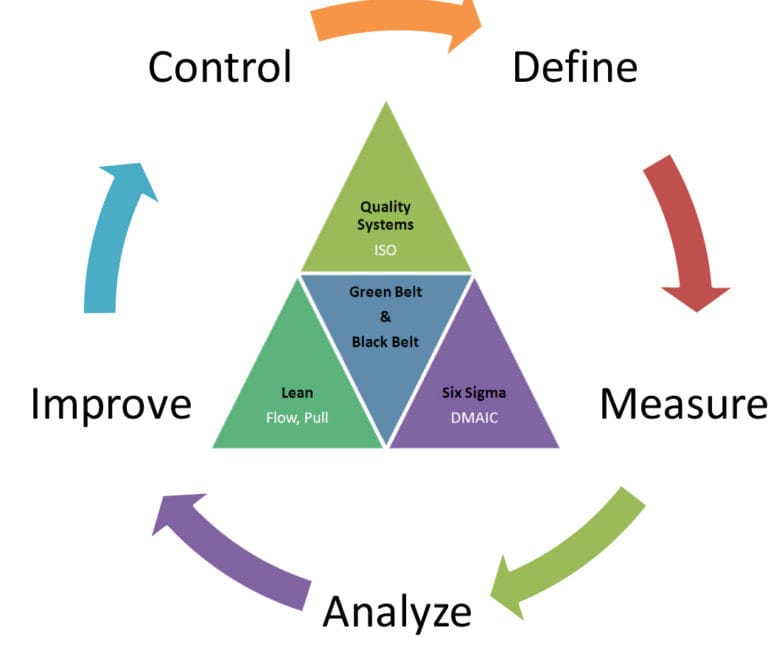
The DMAIC Framework
The basis of Six Sigma lies in its structured methodology, DMAIC, which represents the four steps: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
Define: Find a problem and outline the scope, goals, and specifications of a project.
Measure: Gather the necessary data for establishing current performance baselines.
Analyze: Apply data-driven techniques for ascertaining the root causes of defects and variations.
Improve: Determine solutions to the root cause and introduce better processes.
Control: Monitor improvements to ensure sustained performance and prevent regression.
Six Sigma Roles and Responsibilities
Six Sigma follows a hierarchical structure with specific roles that drive projects:
Yellow Belts: These are team members who understand the basic principles of Six Sigma and assist in projects.
Green Belts: Professionals who work on projects under the guidance of Black Belts.
Black Belts: Experts who lead projects and mentor Green Belts.
Master Black Belts: Senior professionals responsible for strategic direction and mentoring Black Belts.
Champions: Senior executives who sponsor and advocate for Six Sigma initiatives.
Benefits of Implementing Six Sigma
Organizations adopting the Six Sigma benefit from many features such as follows:
Quality improvements: Reduction of defects and higher degree of customer satisfaction.
Cost effectiveness: Stream-lined processes help to avoid considerable cost overrun.
Better Decision-Making : Data-based approach can minimize guess work.
Productivity increase: Effective processes, reducing the idle period.
Industries That Benefit from Six Sigma
Six Sigma, though often related to manufacturing industries, has principles applicable to all areas:
Healthcare: Reducing medical errors and ensuring better care for patients
IT and Software Development: Better software testing and roll-out processes
Finance: Accuracy in completing transactions and customer service
Retail: Inventory management and supply chain efficiency.
Common Six Sigma Tools
Six Sigma utilizes a variety of tools to analyze and improve processes, such as:
- Pareto Charts
- Fishbone Diagrams
- Control Charts
- Histogram Analysis
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Challenges in Implementing Six Sigma
Organizations still have some issues in implementing these advantages:
Resistance to Change: The employees might not be very keen on new methods.
High Initial Investment: Training and certification are costly in the beginning.
Data Dependency: Success depends highly on the data collected and analyzed.
Six Sigma Certification
Six Sigma certification for professionals can boost their careers with the validation of their expertise in the following areas:
Yellow Belt Certification: A basic understanding of the principles of Six Sigma.
Green Belt Certification: Intermediate knowledge and project management skills.
Black Belt Certification: Advanced problem-solving and leadership abilities.
Master Black Belt Certification: Strategic-level expertise and organizational impact.
Six Sigma vs. Lean
While both are process improvement initiatives, Six Sigma and Lean vary in approach.
Six Sigma: Focuses on reducing variation and defects through the use of statistical methods.
Lean: Focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value for the customer.
When brought together, Lean Six Sigma forms a powerful methodology that combines the strengths of each.
Case Studies of Six Sigma Success
Motorola: Credited for the invention of Six Sigma, Motorola saved billions in terms of quality improvements.
General Electric: GE has recorded over $10 billion in savings due to Six Sigma’s embedment in their culture.
Amazon: Six Sigma helped Amazon improve its supply chain management and satisfied its customers better.
The Future of Six Sigma
With the advancements in technology, Six Sigma is changing to integrate digital tools, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies allow for more accurate data analysis, predictive modeling, and automation, which make Six Sigma even more effective.
5S Methodology – What are The Five S’s?
Conclusion
Six Sigma is more than a methodology; it is a mindset that fosters continuous improvement, operational excellence, and customer satisfaction. Whether you’re a professional seeking to enhance your skills or an organization aiming to stay competitive, adopting Six Sigma principles is a proven way to achieve lasting success.
FAQs on Six Sigma
1. What is Six Sigma?
This is a data-driven methodology aimed to simplify business processes by trying to reduce defects, minimize variability, and enhance quality. It aims to have a defect rate of less than 3.4 defects per million opportunities in DPMO.
2. What are the main goals of Six Sigma?
- Improve process efficiency.
- Enhance product and service quality.
- Reduce operational costs.
- Increase customer satisfaction.
- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
3. What is the meaning of the term “Sigma”?
It may range from weeks to months based on the project scope and complexity. Average projects will last for several weeks up to months.
4. What are the key methodologies in Six Sigma?
- DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (used for improving existing processes).
- DMADV: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify (used for designing new processes or products).
5. Who can benefit from Six Sigma?
Six Sigma can be beneficial for:
- Organizations aiming to improve efficiency and quality.
- Professionals seeking to enhance their career prospects.
- Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, IT, finance, retail, and logistics.
6. What are the Six Sigma certifications, and who should pursue them?
- Yellow Belt: For beginners and team members assisting in projects.
- Green Belt: For professionals leading specific projects.
- Black Belt: For leaders and experts managing larger projects.
- Master Black Belt: For seasoned professionals mentoring others and driving strategic initiatives.
7. What are some common tools used in Six Sigma?
- Pareto Chart
- Fishbone Diagram
- Control Charts
- Scatter Diagrams
- Process Mapping
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
8. What is the difference between Six Sigma and Lean?
- Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and process variation.
- Lean emphasizes eliminating waste and improving flow efficiency.
Combined, Lean Six Sigma leverages the strengths of both approaches.
9. What industries use Six Sigma?
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, IT, finance, retail, aerospace, and telecommunications commonly use Six Sigma to enhance processes and reduce costs.
10. How is Six Sigma implemented in an organization?
Implementation involves the following steps:
- Identifying problems and defining objectives.
- Forming a Six Sigma team with certified professionals.
- Applying DMAIC or DMADV methodologies.
- Using data and statistical tools to analyze processes.
- Implementing and monitoring improvements.
11. What are the challenges of adopting Six Sigma?
- Resistance to change.
- High initial investment in training and certification.
- Dependency on accurate data.
- Difficulty in sustaining improvements without proper monitoring.
12. Can Six Sigma be applied to small businesses?
Yes, Six Sigma principles are scalable and can be tailored to suit small businesses. These organizations can benefit from improved processes, reduced costs, and better customer satisfaction.
13. What is the role of leadership in Six Sigma?
Leadership plays a critical role in Six Sigma by:
- Sponsoring and supporting projects.
- Driving cultural change.
- Ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- Providing resources for training and implementation.
14. How does Six Sigma improve customer satisfaction?
By reducing defects and improving process efficiency, Six Sigma ensures higher quality products and services, leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
15. Is Six Sigma relevant in the era of automation and AI?
Absolutely! Six Sigma complements automation and AI by providing a structured framework for process improvement. Advanced technologies enhance data collection, analysis, and process optimization, making Six Sigma even more effective.
16. How long does it take to complete a Six Sigma project?
The duration varies depending on the project scope and complexity. Typical projects can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
17. What are some examples of successful Six Sigma implementation?
- Motorola: Reduced manufacturing defects and saved billions.
- General Electric: Achieved over $10 billion in savings.
- Amazon: Optimized supply chain processes and enhanced customer satisfaction.
18. How do I get certified in Six Sigma?
You can obtain Six Sigma certification through accredited institutions or online platforms. Training programs are available for all levels, from Yellow Belt to Master Black Belt.
19. How is success measured in Six Sigma?
Success is measured through:
- Reduction in defects.
- Improved customer satisfaction scores.
- Cost savings.
- Enhanced process efficiency.
20. Can Six Sigma principles be applied in everyday life?
Yes, Six Sigma concepts like waste reduction, data-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement can be applied to personal productivity, time management, and problem-solving in daily life.
